Understanding Ibogaine and Its Uses
Ibogaine, a plant alkaloid derived from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, has gained attention for its promising anti-addictive properties. As a psychedelic medicine, it shows potential to treat addiction, particularly substance dependence and acute opioid withdrawal. However, there may be possible Fatal Outcomes During Ibogaine Treatment. You Need to Know before you undergo an ibogaine treatment!

Despite its therapeutic promise, there are significant safety concerns, particularly related to cardiac toxicity and the risk of heart attack due to ibogaine ingestion.
However, this doesn’t happen very often at all—it’s estimated that less than 1% of those undergoing ibogaine therapy experience this problem.
Under the Fatal Outcomes During Ibogaine Treatment, we will cover;
Opioid Dependence and Heroin Addiction and Ibogaine Therapy
Treating Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction is a major public health crisis, with many seeking effective treatments. Ibogaine appears to be a viable option due to its anti-addictive properties.
It has shown potential in alleviating withdrawal symptoms, making it a hopeful therapeutic drug for those undergoing opioid detoxification. Ibogaine’s ability to alleviate withdrawal symptoms makes it a promising option to treat addiction.
However, the administration of ibogaine must be approached with caution due to its associated cardiac risks. One of the potential cardiac risks is ventricular fibrillation, which can occur due to massive QT prolongation after ingestion of ibogaine.
Mechanism of Action
Ibogaine’s mechanism of action is multifaceted. It interacts with several neurotransmitter systems in the brain, including the serotonin and dopamine systems, which are crucial in addiction.
By modulating these pathways, ibogaine helps reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, offering a unique approach to treating addiction. However, these interactions also contribute to its hallucinogenic effects and potential toxicity.
Cardiac Risks During Ibogaine Administration
Ibogaine consumption can lead to various cardiac arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia and fatal arrhythmia, often due to massive QT prolongation. These adverse effects are linked to its impact on cardiac ion channels and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
Studies have reported ibogaine-associated cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death, emphasizing the need for cardiac monitoring during ibogaine treatment. Controlled trials and further research are essential to understand the full extent of these risks.
Addressing Safety Concerns
Cardiac Monitoring and Long QT Syndrome
One of the critical safety concerns with ibogaine is its potential to induce long QT syndrome, a condition that can lead to life-threatening complications due to ibogaine intoxication, including sudden death. Long QT syndrome affects the heart’s electrical activity, increasing the risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Therefore, it is crucial to monitor the QT interval during ibogaine therapy to mitigate the risk of cardiac arrhythmias and other heart-related adverse effects.
Potential Complications of Ibogaine Use
Increased risk of cardiac toxicity is a significant concern with ibogaine intake. At high doses, ibogaine toxicity can result in serious complications, including sudden cardiac death.
The Drug Enforcement Administration classifies ibogaine as a controlled substance, highlighting the importance of controlled substance regulations to ensure safe administration. Patients should undergo thorough cardiac evaluations and continuous monitoring during treatment to prevent potential complications.
Managing Adverse Effects
Managing the adverse effects of ibogaine is crucial for its safe use in treating addiction. Health practitioners should be prepared to address issues such as hypertension, tachycardia, and other cardiovascular problems that may arise during treatment. Emergency medicine protocols should be in place to handle any life-threatening complications promptly.
Certain Factors Increase The Risk Of An Ibogaine Heart Attack.
Certain factors can increase your risk of a heart attack during ibogaine treatment, including:
A family history of heart disease. If you are genetically predisposed to serious heart conditions, it’s important to know the symptoms. Heart attacks are more common in men than women and usually occur between the ages of 45 and 65.
Smoking or other tobacco use. Cigarette smoke harms your blood vessels, which can increase your risk of a stroke or heart attack.
History of previous heart attack, especially if you were taking medications for high blood pressure at the time or have diabetes that’s not well controlled by diet and exercise alone; diabetes increases your chances of dying from a second heart attack within one year after the first one occurs by five times as much as it raises death rates overall (from all causes). The risk is even higher if you’re overweight—a BMI above 27 increases the odds by three times compared with people who weigh less than 20 pounds more than their ideal body weight!
Cardiac arrhythmia is not uncommon during ibogaine treatments, but it’s rarely anything serious. It usually happens when the heart beats too fast or too slow, and that’s why it can cause palpitations, chest pain, and even fainting.
The thing is that some people are more likely to experience an abnormal heart rhythm than others.
People who take certain medications like beta-blockers and antihistamines may be at a higher risk for cardiac problems during treatment because these drugs can slow down your heartbeat or make it difficult for your body to regulate its blood pressure.
If you have any health conditions or concerns about your heart health before starting a course of ibogaine therapy (or any other drug treatment), you should talk with a doctor first so they can help assess whether ibogaine might be safe for you.
How do you know if you are having a heart attack?
You may have a heart attack if you experience any of the following symptoms:
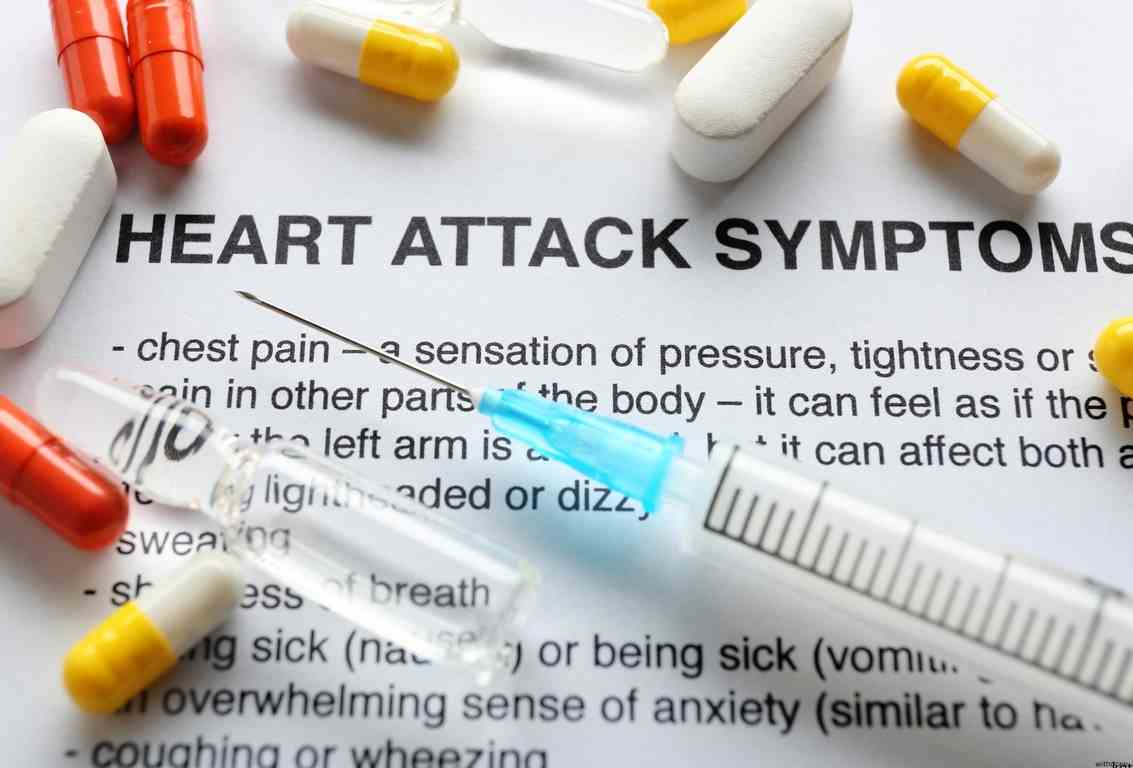
Sweating.
Nausea.
Dizziness.
Shortness of breath.
Palpitations (feeling your heartbeat in your chest). If you’re having these symptoms and are unsure whether they are related to ibogaine treatment, call emergency services immediately for advice on what to do next.
Substance Abuse and Ibogaine Treatment
Treating Substance Dependence
Ibogaine’s anti-addictive properties make it a potential treatment to treat addiction, including various substance dependencies such as alcohol abuse and drug dependence.
However, the risk of ibogaine-induced cardiac toxicity necessitates caution. Internet-purchased ibogaine toxicity poses additional dangers, as unregulated substances can exacerbate adverse effects and increase the likelihood of sudden cardiac incidents.
Therapeutic Concentrations and Controlled Trials
To ensure the safe use of ibogaine in treating addiction, it is vital to establish therapeutic concentrations through controlled trials. These trials can provide insights into the appropriate dosages and administration protocols to minimize cardiac risks.
Monitoring blood pressure and cardiac function during ibogaine therapy is essential to detect any early signs of adverse effects and prevent fatal arrhythmias.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Ibogaine is classified as a controlled substance in many countries, including the United States. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has placed ibogaine in Schedule I, indicating a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use.
This classification limits research and clinical use, posing a challenge to its integration into mainstream addiction treatment. Advocacy for reclassification and controlled clinical trials could help unlock its potential benefits while ensuring safety.
You can also read: Why Is Ibogaine Illegal?
The Role of Ibogaine in Treating Addiction
Psychedelic Medicine and Addiction
As a psychedelic medicine, ibogaine offers a unique approach to treating addiction. Unlike conventional therapies that primarily address the physical aspects of addiction, ibogaine also targets the psychological components.
Its hallucinogenic effects can lead to profound introspective experiences, helping individuals address the underlying causes of their substance abuse. However, these effects also necessitate a controlled and supportive environment to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Integrating Ibogaine into Addiction Treatment Programs
For ibogaine to become a mainstream treatment option, it must be integrated into comprehensive addiction treatment programs.
This integration involves collaboration between medical professionals, addiction specialists, and regulatory bodies. Ensuring that patients receive holistic care, including psychological support and medical monitoring, is essential for maximizing the benefits of ibogaine while minimizing risks.
Future Directions and Research
Developing Safer Alternatives
Given the cardiac risks associated with ibogaine, developing safer alternatives with similar anti-addictive properties is a promising avenue for future research.
These alternatives could offer the benefits of ibogaine without the associated cardiac toxicity, providing a safer option for treating addiction. Innovations in drug design and delivery methods could lead to breakthroughs in addiction therapy.
Policy and Advocacy
Advocacy for policy changes that support ibogaine research and controlled clinical use is crucial for advancing its role in addiction treatment. Policymakers, researchers, and healthcare professionals must work together to create a regulatory framework that balances safety with the potential benefits of ibogaine.
Public awareness campaigns can also help reduce stigma and promote informed discussions about ibogaine’s therapeutic potential.
Addressing the Risks of Ibogaine Administration
Monitoring and Mitigating Risks
Effective management of the risks associated with ibogaine treatment involves comprehensive monitoring and mitigation strategies. Patients undergoing ibogaine therapy should have continuous cardiac monitoring to detect any changes in the QT interval.
Pre-treatment assessments, including a thorough medical history and electrocardiograms (ECGs), can help identify individuals at higher risk of cardiac complications.
Emergency Preparedness
Healthcare providers administering ibogaine must be prepared for potential emergencies. This includes having resuscitation equipment and medications readily available to manage cardiac arrest or severe arrhythmias. Staff should be trained in advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) to respond effectively to adverse events during treatment.
Post-Treatment Care
Post-treatment care is crucial for ensuring the long-term safety and effectiveness of ibogaine therapy. Patients should be monitored for any delayed adverse effects and provided with ongoing support to prevent relapse. This support can include counseling, support groups, and follow-up medical evaluations to ensure sustained recovery.
Understanding the Broader Implications
Societal Impact
The societal impact of ibogaine treatment extends beyond individual patients. Effective addiction treatment can lead to reduced crime rates, lower healthcare costs, and improved quality of life for individuals and communities. However, the potential benefits must be weighed against the risks, necessitating a balanced and informed approach to ibogaine therapy.
Ethical Considerations
The use of ibogaine in addiction treatment raises several ethical considerations. Informed consent is paramount, with patients needing a clear understanding of the potential risks and benefits.
Additionally, equitable access to ibogaine treatment must be addressed to ensure that all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status, can benefit from this potentially life-saving therapy.
Global Perspectives
Ibogaine’s status as a controlled substance varies globally, influencing its availability and use. Countries with more progressive drug policies may offer greater opportunities for ibogaine research and treatment, while others may impose strict regulations that limit access. Understanding these global perspectives can inform policy development and promote international collaboration in addiction treatment research.
The Future of Ibogaine Research
Technological Advances
Advances in technology are likely to play a significant role in the future of ibogaine research. Innovations in imaging techniques, such as functional MRI, can provide insights into the neurobiological effects of ibogaine.
Additionally, advancements in genetic testing may help identify individuals who are more likely to benefit from ibogaine therapy, further personalizing addiction treatment.
You can also read Could Ibogaine Be The Key To Ending Drug Addiction?
Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches that combine pharmacology, psychology, and cardiology are essential for advancing ibogaine research. Collaboration between these fields can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of ibogaine’s effects and the development of safer, more effective treatment protocols.
Public Engagement
Engaging the public in discussions about ibogaine and addiction treatment is crucial for reducing stigma and promoting informed decision-making. Public education campaigns can highlight the potential benefits and risks of ibogaine, encouraging individuals to seek evidence-based treatments and addiction support.
Conclusion
Ibogaine offers a promising approach to treating addiction, particularly for those struggling with opioid dependence and substance abuse. However, the potential cardiac risks, including long QT syndrome and cardiac arrhythmias, necessitate careful consideration and monitoring.
Controlled trials, regulatory oversight, and thorough cardiac evaluations are crucial to harnessing ibogaine’s therapeutic benefits while ensuring patient safety. As we continue to explore ibogaine’s potential, addressing safety concerns remains paramount to prevent life-threatening complications and promote effective addiction treatment.
By expanding our understanding of ibogaine’s effects, advocating for safe and controlled use, and exploring alternative treatments, we can unlock new possibilities in the fight against addiction.
The journey to integrating ibogaine into mainstream medicine is complex. Still, with careful research and collaboration, it holds the potential to transform addiction therapy and offer hope to countless individuals struggling with substance abuse.


