As we delve into this topic, Who Is An Addict? let’s take a moment to ponder. When you encounter someone who simply cannot imagine life without something, how do you categorize them? Would you boldly label this person as an addict? To call someone an addict implies a deep passion for a specific activity or substance, dedicating a significant amount of time to indulging in it.
Table of Contents

So why do people get addicted? Addiction leads to dependence. Addiction also causes tolerance and withdrawal symptoms.
People can get addicted to many things. For example, some people are addicted to drugs, alcohol, and gambling. Alcohol use disorder is the most common substance addiction in the United States, with about 10% of people aged 12 or older in the U.S. having this disorder.
Others have an addiction to sex or overeating food. Or they become so obsessed with something that it makes them behave dangerously or badly towards friends and family. This can cause problems in their lives that they can’t control.
Some people have problems with more than one addiction – for instance, someone might be addicted to drugs but have a drinking problem as well. People who are addicts need help and support not just from friends but others trained in helping them overcome these addictions. Ibogaine clinics are also an option for those seeking alternative treatments for addiction.
Who Is An Addict?
So a dictionary definition of an addict reads thus a person with an uncontrolled compulsion to continue engaging in an activity despite suffering negative personal or professional consequences:
If you say that someone is an addict, you mean that they like a particular activity or substance very much and spend as much time doing it as they can.
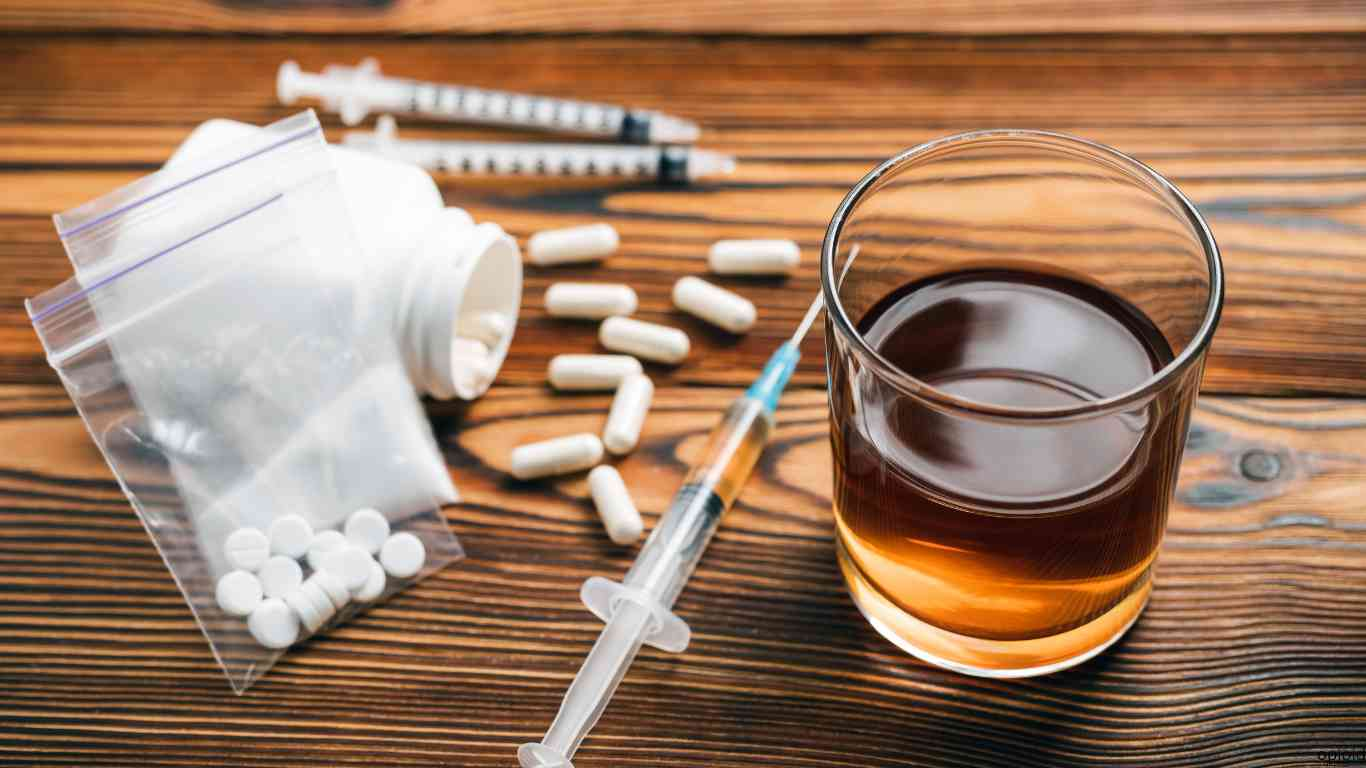
In this context of ours, an addict is a man or woman whose life is controlled by drugs. Perhaps you admit you have a problem with drugs, but you don’t consider yourself an addict.
Is it shameful to be an Addict?
Everyone has preconceived ideas about what or who an addict is. There is nothing shameful about being an addict once you begin to take positive actions to get yourself clean from the substance or whatever thing you may be addicted to.
Most of the time, people tend to get involved in drugs on their own due to certain conditions that they may be going through in their life or family. I mean, those who are addicted tend to lie to doctors about a certain condition to get a prescription drug that is addictive, while others go as far as stealing to get their hands on the drugs. From one drug, they tend to move to another in a bid to counter the effects of the other.
This, in most cases, makes them reliable and dependent on these drugs, which makes them addicted to them and exposed to a lot of dangers like getting arrested or even death in a worst-case scenario.
When someone becomes an addict, they use all means possible to get the substance they are addicted to, no matter the cost. Even if they can’t afford it, they will seek financial assistance from friends or family members, with some lying to them about what they want to do with the money, putting their addiction ahead of their financial responsibilities.
When you become addicted to these drugs, a trip to the rehab center is unavoidable for those who have the willingness to accept that they are suffering from addiction. At the same time, jail cells welcome those who are adamant and won’t quit using especially illegal substances.
Once into drugs, it may feel impossible or difficult for an addict to stop using them cause the brain has been rewired by the drug, especially cocaine and other meths. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in prescribing and monitoring medicines to prevent addiction and ensure safe usage, emphasizing the importance of following instructions and seeking guidance from a healthcare professional.
Understanding Drug Dependence and Withdrawal
Drug dependence occurs when an individual’s body adapts to the presence of a substance, necessitating higher doses to achieve the same effect. This dependence can lead to serious side effects, health complications, and even death. Effective treatment must address the root causes of addiction, which often include post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and traumatic brain injuries (TBI), conditions frequently encountered among military veterans.
The Nature of Substance Use Disorders
Substance use disorders are characterized by the inability to control the use of drugs or alcohol despite negative consequences. Addiction develops as individuals continue to seek the pleasurable effects of substances to cope with stress, trauma, or emotional pain.
This behavior creates a cycle of abuse and dependence that is difficult to break without professional intervention.
Why Do People Get Addicted?
Exploring the Root Causes of Drug Addiction
Addiction is not merely a result of poor choices or lack of willpower; it is a complex interplay of genetic, biological, psychological, social, and environmental factors. Understanding these root causes is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Genetic Predisposition:
Genetics plays a significant role in addiction susceptibility. Individuals with a family history of addiction are more likely to develop similar patterns of substance use.

Specific genes can influence how the brain responds to drugs and alcohol, affecting vulnerability to addiction.
Biological Factors:
Neurobiology plays a critical role in addiction.
Drugs and alcohol alter the brain’s neurotransmitter systems, particularly those involved in reward, motivation, and decision-making. Continued substance use can lead to changes in brain structure and function, perpetuating addictive behaviors.
Psychological Factors:
Mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are closely linked to addiction. Individuals may turn to substances as a way to self-medicate or alleviate emotional distress.
It is important to consult with a mental health professional for planning and conducting interventions.
Social and Environmental Influences:
Environmental factors significantly impact addiction risk.

Peer pressure, exposure to substance use within the family or community, and stressful life circumstances (e.g., poverty, trauma, abuse) can contribute to the development of addictive behaviors. Socioeconomic factors, including access to healthcare and education, also play a role.
Developmental Factors:
Early exposure to substances during adolescence, when the brain is still developing, can increase the likelihood of addiction later in life. Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), such as neglect, abuse, or parental substance use, can also contribute to the development of addiction.
Dual Diagnosis:
Many individuals with addiction also have co-occurring mental health disorders, known as dual diagnosis or co-occurring disorders. Treating both conditions simultaneously is essential for successful recovery, as untreated mental health issues can exacerbate substance use and vice versa. Traumatic brain injuries can also co-occur with addiction and require integrated treatment.
Behavioral Conditioning:
Over time, repeated exposure to substances can lead to conditioned responses. Environmental cues associated with drug use (e.g., places, people, activities) can trigger intense cravings and contribute to relapse even after a period of abstinence.
Cultural and Societal Factors:
Cultural norms and societal attitudes toward substance use can influence addiction rates. The stigma surrounding addiction may prevent individuals from seeking treatment, while cultural beliefs about substances (e.g., alcohol in social settings) can impact patterns of use.
Personal Choice vs. Disease Model:
Addiction is increasingly recognized as a chronic brain disease rather than a moral failing. The disease model emphasizes the neurobiological changes that occur with addiction and the need for medical intervention, destigmatizing addiction and promoting effective treatment approaches.
Implications for Treatment and Prevention
Understanding the root causes of addiction is critical for developing comprehensive and effective treatment and prevention strategies:
Early Intervention: Addressing risk factors early in life, such as providing mental health support and education, can reduce the likelihood of developing addiction.
Integrated Treatment: Comprehensive treatment should address both substance use and underlying mental health disorders through integrated approaches like dual diagnosis treatment programs.
Holistic Approaches: Holistic treatment approaches that consider biological, psychological, social, and spiritual aspects of addiction can improve outcomes and support long-term recovery. Ibogaine clinics, for instance, offer alternative treatment options for addiction, particularly for those seeking innovative therapies.
Education and Awareness: Public education campaigns that raise awareness about addiction as a disease and reduce stigma can encourage individuals to seek help and support.
Policy and Advocacy: Advocating for policies that support access to evidence-based treatment, harm reduction strategies, and prevention efforts can mitigate the impact of addiction on individuals and communities.
Ibogaine Treatment and Its Role in Addiction Recovery
Ibogaine Treatment is an innovative therapy that utilizes the psychoactive substance ibogaine, derived from the Tabernanthe iboga plant found in central Africa.
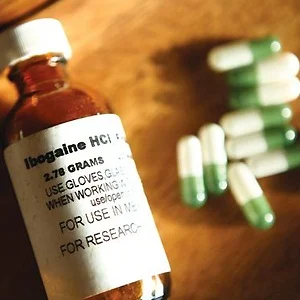
This treatment shows significant promise in addressing various forms of drug addiction, particularly opioid dependence.
Ibogaine Therapy functions by resetting the brain’s neural pathways, thereby reducing cravings and alleviating withdrawal symptoms. Ibogaine clinics offer various levels of support and have shown benefits in treating drug addiction, including opioid dependence, despite the legal status of ibogaine in the U.S., which remains a topic of discussion among researchers and healthcare providers.
Mental Health Professionals play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating addiction. They collaborate with healthcare providers and addiction medicine specialists to create individualized treatment plans. These plans often include a combination of counseling, medication-assisted treatment (MAT) such as methadone for opioid dependence, and participation in support groups.
It is important to note that addiction extends beyond drug abuse to encompass behavioral addictions such as gambling and compulsive spending. Ibogaine has the potential to ease the agony of opioid withdrawal and prevent relapse, providing a promising option for those struggling with opioid addiction.
Challenges and Controversies in Addiction Treatment and Withdrawal Symptoms
Despite the promising results of Ibogaine Therapy, its use remains controversial due to potential risks and side effects. Heart complications and other serious health issues have been reported, highlighting the need for careful medical supervision and thorough patient screening.
Additionally, legal restrictions in many countries limit the availability of ibogaine, making it an inaccessible option for many who might benefit from it.
Solutions Available for Addicts
1. Family, Support Systems, and Support Groups
Family Members play a crucial role in the recovery process by offering support and encouragement. Addiction impacts not only the individual but also their loved ones, leading to strained relationships and emotional turmoil.
Support groups and treatment programs that incorporate family therapy can help mend these relationships and provide a strong support network for both the addict and their family.
The Journey to Overcoming Addiction
Overcoming addiction is a challenging journey that necessitates a combination of medical, psychological, and social interventions. Personalized treatment plans should consider the unique circumstances and needs of the individual.
This often involves a blend of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication-assisted treatment, and holistic approaches like ibogaine therapy. Ibogaine clinics play a crucial role in providing alternative treatment options for those on the journey to overcoming addiction.
The Importance of Support and Follow-Up
Support from mental health professionals, healthcare providers, and support groups is essential for maintaining long-term recovery. Regular follow-up and adjustments to the treatment plan are necessary to address potential relapses or emerging issues. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in monitoring and adjusting treatment plans to ensure safe usage and prevent addiction.

Education about the dangers of drug abuse, effective coping strategies, and the establishment of a robust support system are critical components of successful treatment.
2. Holistic Treatment
Effective addiction treatment often requires a holistic approach that addresses all aspects of the individual’s life. This can include:
Medical Interventions: Using medications to manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. This includes Medication-Assisted Treatment with drugs like methadone and buprenorphine.
Therapeutic Interventions: Engaging in various forms of therapy, including Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which helps individuals understand and change their patterns of thinking and behavior related to addiction.
Support Systems: Participating in support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA), which provide a community of individuals who understand the challenges of addiction.
Holistic Treatments: Incorporating treatments such as Ibogaine Therapy offers a unique approach to addressing the physical and psychological aspects of addiction. Additionally, ibogaine therapy has shown potential in treating traumatic brain injury, with studies indicating marked improvements in disability, psychiatric symptoms, and cognition among military veterans. Ibogaine clinics play a crucial role in providing these holistic treatment options, addressing both the physical and mental health aspects of addiction.
Family Involvement: Engaging family members in the treatment process to rebuild relationships and create a supportive environment for recovery.
So let’s conclude by asking and attempting an answer to this question, which goes thus: Who can become addicted to drugs? The short answer is that anyone can become an addict, whether young or old, rich or poor, male or female.
A lot of us have an idea in our heads about what a person addicted to drugs looks like. But the truth is, anyone can become addicted to drugs. Addiction is when you feel a strong urge to keep taking a drug, even if it is causing harm.
To stop, ask for help. Drug addiction doesn’t depend on your income, your job, age, race, or color. Addiction is a disease of the brain, and it can happen to anyone. Get Ibogaine
3. Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals are indispensable in the diagnosis and treatment of addiction. They collaborate with healthcare providers and addiction medicine specialists to develop individualized treatment plans.
These plans often include a combination of counseling, medication-assisted treatment (MAT) such as methadone for opioid dependence, and participation in support groups. Addressing addiction is not limited to drug abuse but also extends to behavioral addictions like gambling and compulsive spending.
The Future of Addiction Treatment
Advances in medical research and a growing understanding of the complexities of addiction are paving the way for more effective and personalized treatment options. Clinical Trials continue to explore new medications and therapies, while an increasing emphasis on mental health is leading to more comprehensive and integrated treatment approaches.
Additionally, the potential role of ibogaine clinics in addressing addiction, particularly opioid addiction, is gaining interest from researchers and lawmakers as they explore its benefits and challenges.
Final Thoughts
Addiction is a complex and challenging disorder that affects every aspect of an individual’s life. A comprehensive, personalized approach to treatment is essential for achieving long-term recovery.
Ibogaine Therapy, combined with traditional treatments and robust support systems, offers hope for those struggling with addiction. By addressing the underlying causes and providing continuous support, individuals can overcome addiction and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
The journey to recovery is a lifelong commitment that requires dedication, support, and a willingness to embrace change. With the right resources and a strong support system, overcoming addiction is possible, leading to a brighter and more hopeful future.
Conclusion
Addiction is a complex disorder that impacts many aspects of an individual’s life and requires a comprehensive and personalized approach to treatment. Ibogaine Therapy, when integrated with other treatments and support systems, offers hope to those battling addiction. By addressing the underlying causes and providing continuous support, individuals can achieve long-term recovery and improve their overall quality of life.
Effective treatment options, ongoing support from mental health professionals, and a strong network of family and support groups are critical in overcoming addiction and paving the way for a healthier, more fulfilling life.


